Regulatory compliance has become a driving force behind the widespread adoption of electronic invoicing (e-invoicing). Governments worldwide are increasingly implementing regulatory frameworks to streamline tax collection, combat tax evasion, and enhance fiscal transparency.
This blog post explores the impact of these regulatory changes, Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) models, and the integration of emerging technologies based on insights from Billentis’ latest report on e-invoicing on e-invoicing and tax compliance.
Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC)
Definition and types of CTC models
Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) models represent a significant shift from traditional tax reporting methods to real-time or near-real-time transaction monitoring. Under CTC, businesses are required to report invoice data to tax authorities either before or immediately after issuing invoices, ensuring timely and accurate tax reporting. There are several types of CTC models:
- Real-time reporting: In this model, invoices are reported to tax authorities shortly after issuance. Countries like Hungary and South Korea have adopted this approach, requiring businesses to submit invoice data within 24-72 hours of issuance.
- Clearance: This model involves submitting invoices to tax authorities for approval before sending them to the buyer. The clearance process ensures that invoices comply with tax regulations. Countries like Chile and Mexico utilize this model, with variations in the timing of submission and approval.
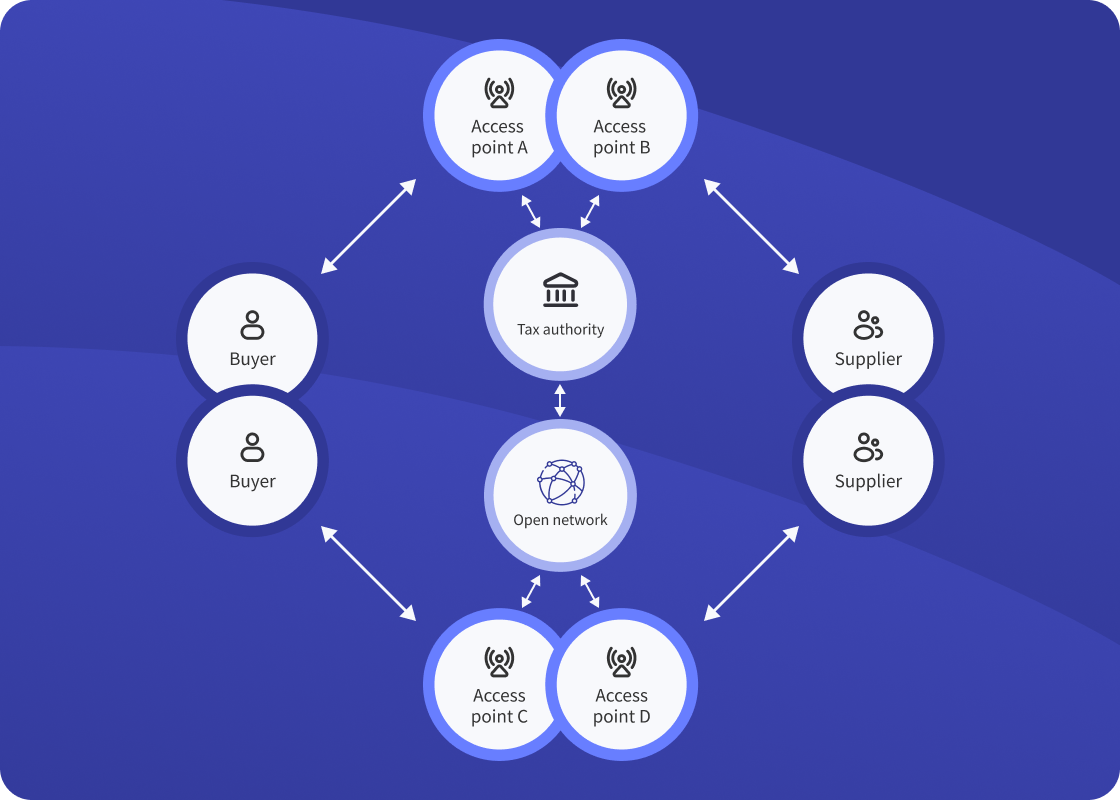
- Centralized exchange: In this model, a central platform facilitates the exchange of electronic invoices between buyers and sellers, incorporating tax reporting functionalities. Italy, Serbia, and Turkey are examples of countries using centralized exchange models.
- Decentralized CTC (5-corner model): This emerging model involves certified service providers handling data validation and exchange. The primary document flow occurs between service providers, with only a subset of the data reported to tax authorities. France and the United Arab Emirates are planning to implement this model.
The shift from periodic to continuous transaction controls
Historically, tax reporting was conducted periodically, often resulting in delayed detection of tax evasion and compliance issues. The shift from periodic transaction controls to continuous transaction controls offers several advantages, as described in the market report from Billentis:
- Faster data availability: Real-time or near-real-time reporting ensures tax authorities have timely access to transaction data, enabling quicker identification of discrepancies and fraudulent activities.
- Enhanced compliance: Continuous monitoring helps businesses adhere to tax regulations more effectively, reducing the risk of penalties and fines.
- Improved fiscal transparency: Regular reporting increases transparency in business transactions, fostering trust between businesses and tax authorities.
Regulatory initiatives and their impact
ViDA — European Union’s VAT in the Digital Age initiative
The European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of implementing e-invoicing regulations to enhance tax compliance. The “VAT in the Digital Age” (ViDA) initiative, announced in December 2022, mandates mandatory intra-community electronic invoicing and business-to-business (B2B) digital reporting by 2028. This initiative aims to:
- Standardize e-invoicing: Ensure that all businesses within the EU exchange invoices electronically, eliminating the need for paper-based processes.
- Enhance tax reporting: Facilitate real-time or near-real-time transaction data reporting to tax authorities, reducing the VAT gap and increasing tax revenue.
- Promote interoperability: Align business and technical interoperability standards across EU member states, simplifying cross-border transactions.
Latin American models for VAT compliance
Latin American countries have pioneered the implementation of e-invoicing and CTC models to combat tax evasion and improve tax collection efficiency. For instance:
- Brazil: The Nota Fiscal Eletrônica (NF-e) system requires businesses to issue electronic invoices, which are submitted to tax authorities for validation before goods are dispatched. This system has significantly reduced tax evasion and increased tax revenue.
- Mexico: The Comprobante Fiscal Digital por Internet (CFDI) system mandates the electronic issuance of invoices and their submission to tax authorities for validation. This model has streamlined tax compliance and improved fiscal transparency.
Digital reporting requirements (DRR) and reducing the VAT gap
The VAT gap, representing the difference between expected tax revenue and the amount collected, has long been a concern for governments. Digital Reporting Requirements (DRR) help bridge this gap by ensuring accurate and timely reporting of tax-related data. The Billentis market report states that countries implementing DRR have seen significant reductions in their VAT gaps. For example:
- Italy: The introduction of e-invoicing and digital reporting requirements has resulted in an annual increase in tax revenue of approximately €6 billion.
- Chile and Mexico: By implementing CTC models, these countries have reduced their VAT gaps by up to 50%.
Technology and compliance
Integration of emerging technologies
Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain are crucial in enhancing e-invoicing and tax compliance processes. The report lists several promising benefits:
- Artificial intelligence: AI can automate the validation and processing of invoices, detect anomalies, and ensure compliance with tax regulations. It can also match invoices with purchase orders and delivery receipts, reducing errors and discrepancies.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology provides a secure and immutable ledger for recording transactions. It ensures the authenticity and integrity of invoice data, making it easier for tax authorities to audit and verify transactions.
Case studies of successful compliance through technology
- AI in e-Invoicing: Some businesses are leveraging AI to automate their invoicing processes, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and reducing manual errors. For example, AI-powered invoice processing systems can automatically extract and validate data from invoices, streamline workflows, and improve accuracy.
- Blockchain for tax compliance: Blockchain creates transparent and tamper-proof transaction records. This technology helps businesses comply with regulatory requirements and provides tax authorities with a reliable transaction data source.
As regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, businesses must stay informed and adapt to these changes to remain competitive and compliant. Embracing e-invoicing and leveraging advanced technologies will not only help businesses meet regulatory requirements but also unlock significant operational benefits, positioning them for success in the digital age. Download the market report for more insights.