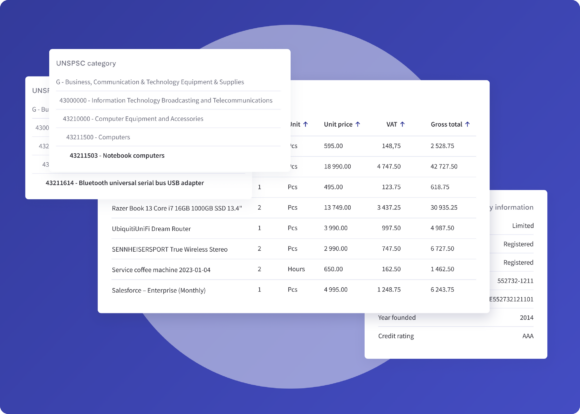
Transactions, technologies and trends
Category: Accounting
Accounting is the systematic process of recording, summarizing, analyzing, and interpreting financial transactions and information within an organization. It serves as the foundation for monitoring the financial health of a business, facilitating informed decision-making, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
At its core, accounting involves the following key aspects:
- Recording Transactions: Accountants meticulously record all financial activities, including sales, purchases, expenses, and revenue, in an organized and standardized manner. These transactions are documented in financial statements, journals, and ledgers.
- Financial Statements: These documents, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, provide a snapshot of a company’s financial position, performance, and cash flow. They help stakeholders evaluate profitability, liquidity, and overall stability.
- Summarization and Classification: Accountants categorize transactions into different accounts, creating a clear structure that facilitates analysis. Common accounts include assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses.
- Double-Entry System: Accounting relies on the double-entry system, where each transaction affects at least two accounts with equal and opposite entries. This ensures that debits and credits are always balanced and accurate.
- Financial Analysis: Accountants interpret financial data to provide insights into a company’s financial health, trends, and performance. This analysis assists managers, investors, and stakeholders in making informed decisions.
- Auditing and Compliance: Auditors verify the accuracy of financial records, ensuring they adhere to established accounting standards and legal requirements. This process enhances transparency and instills confidence in financial reporting.
- Management Accounting: In addition to external financial reporting, accounting supports internal decision-making through management accounting. This involves generating reports, budgets, and forecasts to guide operational and strategic choices.
- Taxation: Accounting plays a critical role in calculating and reporting taxes accurately, minimizing the risk of non-compliance and optimizing tax strategies.
In today’s complex business landscape, accounting software and technology have revolutionized the field, automating routine tasks and enabling real-time access to financial data. This transformation enhances efficiency, accuracy, and the ability to respond swiftly to changing financial conditions.
Ultimately, accounting serves as a vital tool for organizations to maintain financial transparency, meet regulatory requirements, attract investors, and navigate the intricate financial landscape with confidence.
Read our blog articles to learn more about how accounting is changing in an increasingly digital world.
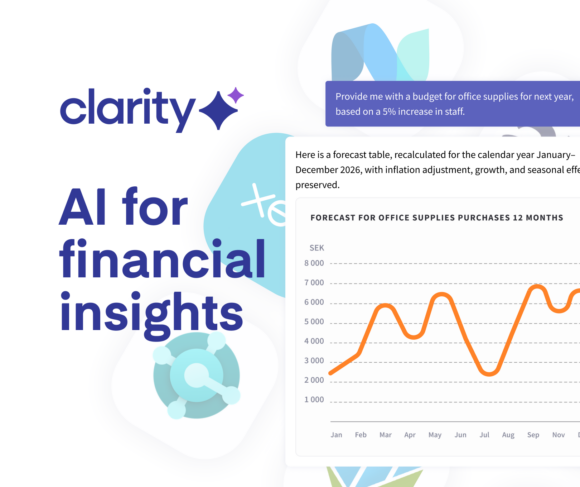
We’re introducing Clarity — the AI agent for financial insights.
Clarity is developed to provide finance, accounting, and procurement professionals with the insights they need to make confident, data-driven decisions.

Data is the fuel of the AI paradigm. Here’s why modern data management has become increasingly important for businesses and financial processes.

Artificial intelligence is reshaping business operations and finance is no exception. Our latest whitepaper provides an overview of AI in finance and accounting, explores practical use cases, and outlines how to get started with implementation.

The European Union’s VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) initiative is a comprehensive reform to modernize the VAT system across the EU. Here’s what you need to know about ViDA.
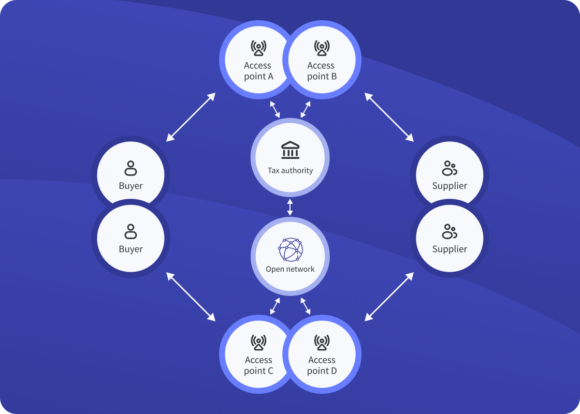
Regulatory compliance has become a driving force behind the widespread adoption of e-invoicing. This blog post explores the impact of these regulatory changes